Helium Leak Testing
Jargon of Helium Leak Testing
Before we get into the description, it is better to know the jargon used in the process
- Helium - is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, trace, mobile, monatomic gas with one of the smallest molecular sizes.
Helium Leak Testing
Using Helium to check leak in parts is highly effective compared to leak testing using normal atmospheric air. Helium Leak Testing is a type of non-destructive quality control testing of manufactured parts to ensure fluids do not leak into or out of the part. Depending on the material of the part and the criticality of the application of the part, leak rates to the extent of 1×10-12mbar.l.sec -1 need to be detected and measured.
Helium being a colourless, odourless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, trace, mobile, monatomic gas with one of the smallest molecular sizes, allows detection of extremely low leak rates with high accuracy and sensitivity. Measurement or quantification of leak rate is achieved through a mass spectrometer.
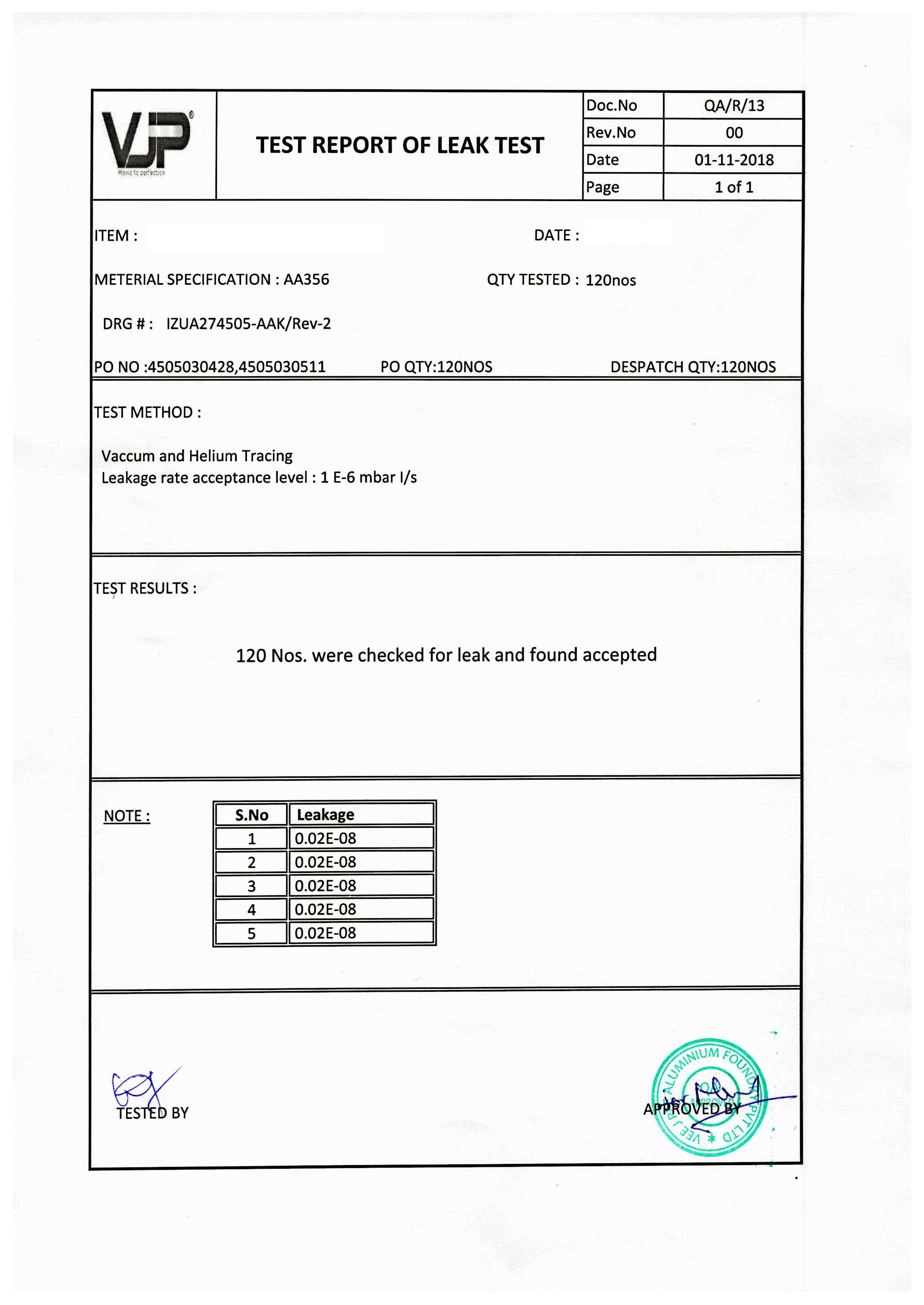
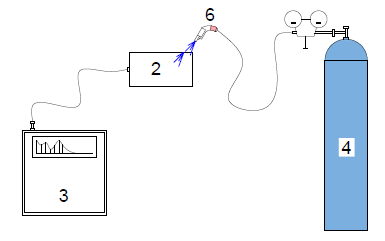
Helium leak test comprises of 1) chamber, 2) part to be tested, 3) leak detector with mass spectrometer 4) helium cylinder 5) connecting hoses and 6) sniffer or sprayer
Methods of Helium Leak Detection
There are two methods of helium leak detection, integral testing and local testing. The selection of method depends on the application of the part being tested. The “integral” method shows only if there is a leak (but not the number of different leaks), the “local” method shows the location of a leak. Both of these detection methods can further be divided into two variants: “part under pressure”, and “part under vacuum”.
Integral (part under pressure) method the part under investigation is placed in a vacuum chamber. The part is pressurized with helium to a specified pressure and the chamber is connected to the leak detector. In the case of a leak/leaks in the part, helium from within the part enters into the vacuum chamber and then will be detected by mass spectrometer in the leak detector. The mass spectrometer also quantifies the helium leak rate and is displayed, recorded.
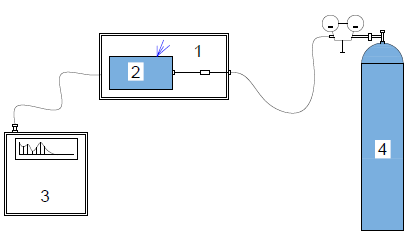
Integral (part under vacuum) method the part under investigation is placed within a chamber pressurised with helium. The part is directly connected to the leak detector. If there is any leak in the part, helium gas from the chamber enters into the part through the leak and then will detected by the mass spectrometer in the leak detector.
Local (part under pressure) method the part under investigation is pressurized with helium gas. A sniffer is moved near/around the part’s likely leak points like welds, flanges, ducts etc., to suck any leaking helium gas. This “sniffed” gas is passed to a mass spectrometer to record any increased helium levels.
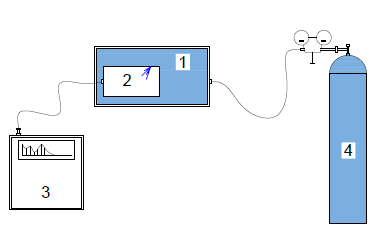
Local (part under vacuum) method the part under investigation is evacuated and helium gas is liberally sprayed near/around the part’s likely leak points. If there is any leak in the part, helium gas will be sucked into the part. The gas, from within the part, is passed into a mass spectrometer to record any increased helium levels.
Application of Helium Leak Testing in industries
- Transformers
- Automotive
- Aviation & Aerospace
- Medical devices
- Heat exchangers, Pressure vessels etc
At VJP
Machined aluminium alloy castings, generally flanges of various grades are tested at our in-house Helium Leak Testing facility to the requirements of various customers by highly qualified inspectors. VJP is equipped with state of the art, Leybold Phoenix Quadro Leak detector.
Leybold Phoenix Quadro Leak detector.
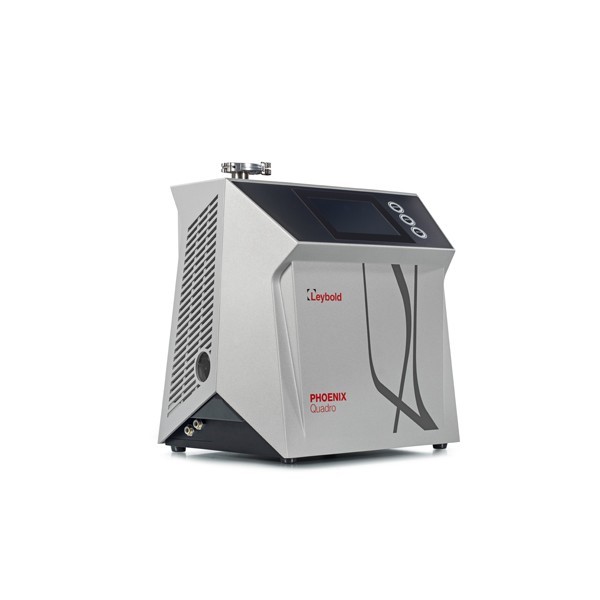

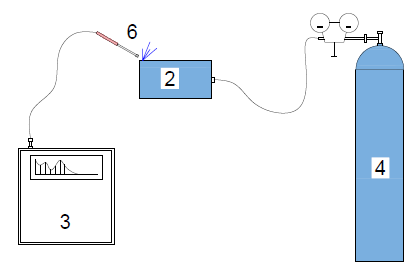
Fig. Test report of leak test